Wi-Fi 6 vs Wi-Fi 6E vs Wi-Fi 7: What’s the Difference?
About
In the ever-evolving world of wireless technology, staying updated on the latest Wi-Fi standards can feel overwhelming. With the introduction of Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E, and the upcoming Wi-Fi 7, it’s essential to understand their differences and how they can impact your internet experience. This blog will break down the key features, benefits, and use cases of each standard to help you decide which one is right for you.
1. Wi-Fi 6: The Foundation of Modern Wireless Networking
Wi-Fi 6, also known as 802.11ax, was introduced in 2019 as a significant upgrade over Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac). It focuses on improving efficiency, speed, and performance in crowded environments.
Key Features of Wi-Fi 6
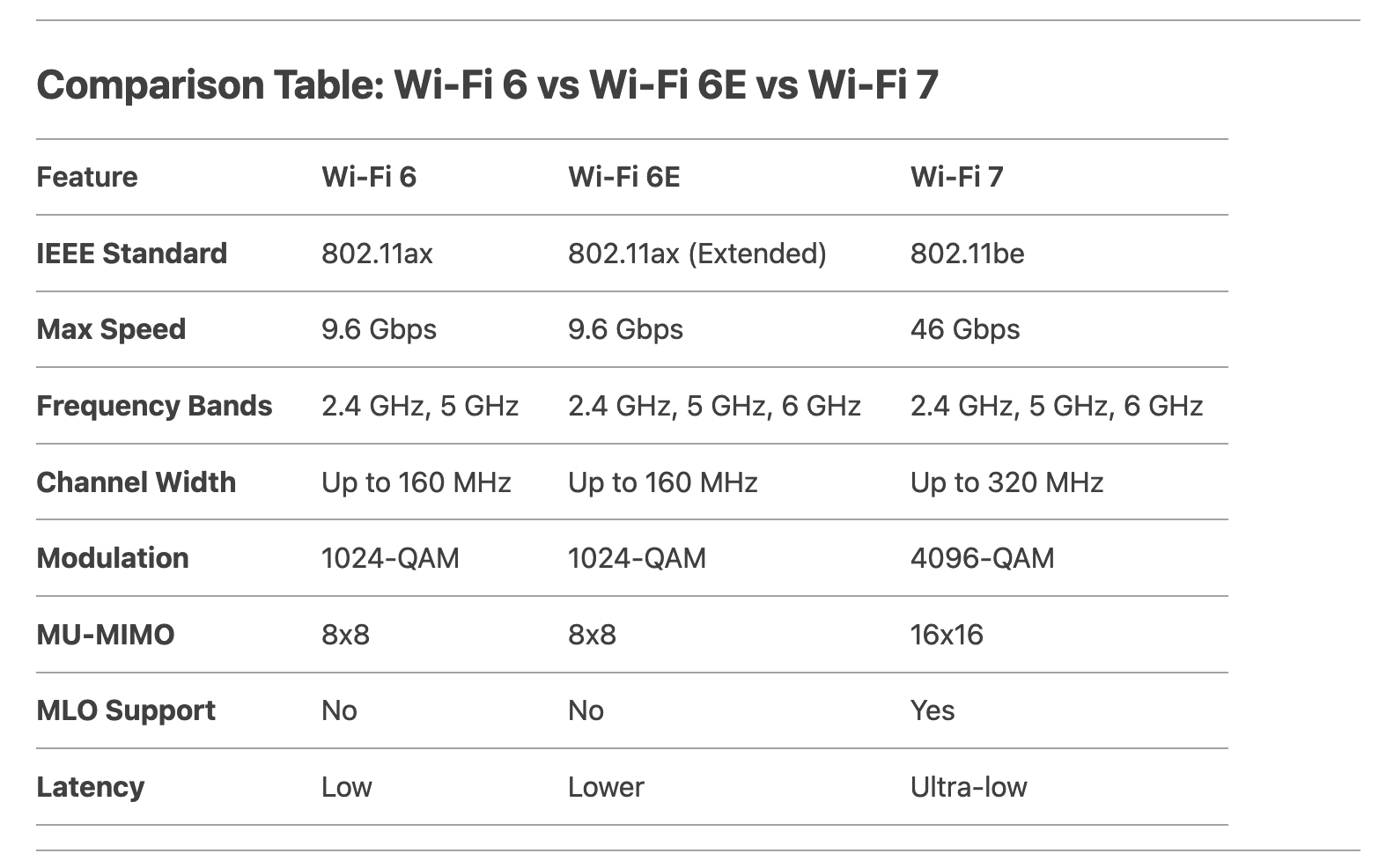
- Speed: Theoretical maximum speed of 9.6 Gbps, though real-world speeds are typically lower19.
- Frequency Bands: Operates on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands112.
- OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access): Allows multiple devices to share a channel, reducing latency and improving efficiency912.
- MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output): Supports up to 8 simultaneous data streams, enhancing performance in multi-device households112.
- 1024-QAM Modulation: Increases data throughput by packing more data into each signal912.
Best Use Cases for Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 is ideal for homes and offices with multiple connected devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and smart home gadgets. It’s a cost-effective upgrade for those looking to improve network efficiency without breaking the bank712.
2. Wi-Fi 6E: Expanding the Spectrum
Wi-Fi 6E, introduced in 2021, is an extension of Wi-Fi 6 that adds support for the 6 GHz frequency band. This new band provides additional spectrum, reducing congestion and interference in crowded networks.
Key Features of Wi-Fi 6E
- 6 GHz Band: Offers up to 1,200 MHz of additional spectrum, enabling faster speeds and lower latency110.
- Wider Channels: Supports 160 MHz channels, which are ideal for high-bandwidth activities like 4K streaming and gaming1012.
- Backward Compatibility: Works with Wi-Fi 6 devices but requires 6E-compatible devices to access the 6 GHz band911.
Best Use Cases for Wi-Fi 6E
Wi-Fi 6E is perfect for environments with high device density, such as apartment buildings, offices, and smart homes. It’s particularly beneficial for applications requiring low latency, like VR gaming and 4K video streaming1012.
3. Wi-Fi 7: The Future of Wireless Connectivity
Wi-Fi 7, also known as 802.11be, is the next-generation standard set to revolutionize wireless networking. Expected to be fully adopted by 2024, it promises unprecedented speeds, lower latency, and advanced features.
Key Features of Wi-Fi 7
- Speed: Theoretical maximum speed of up to 46 Gbps, nearly five times faster than Wi-Fi 6E110.
- 320 MHz Channels: Doubles the channel width of Wi-Fi 6E, significantly increasing data throughput1012.
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO): Allows devices to connect across multiple bands simultaneously, improving reliability and reducing latency1012.
- 4096-QAM Modulation: Further increases data density, enabling faster and more efficient transmissions110.
- Enhanced MU-MIMO: Supports up to 16 spatial streams, accommodating more devices with improved performance1012.
Best Use Cases for Wi-Fi 7
Wi-Fi 7 is designed for cutting-edge applications like 8K video streaming, AR/VR, and cloud gaming. It’s ideal for tech enthusiasts and businesses that require ultra-high speeds and minimal latency1012.
Which One Should You Choose?
- Wi-Fi 6: A great choice for most households, offering improved speed and efficiency over older standards at an affordable price712.
- Wi-Fi 6E: Ideal for high-density environments and users who need low latency for activities like gaming and streaming1012.
- Wi-Fi 7: Best for future-proofing your network, especially if you’re into advanced applications like AR/VR or 8K streaming. However, it’s currently expensive and requires compatible devices1012.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi 6, 6E, and 7 each offer unique benefits tailored to different needs. While Wi-Fi 6 is sufficient for most users, Wi-Fi 6E provides additional spectrum for less congestion, and Wi-Fi 7 represents the future of wireless connectivity with groundbreaking speeds and features. Consider your specific requirements and budget when choosing the right standard for your home or business.